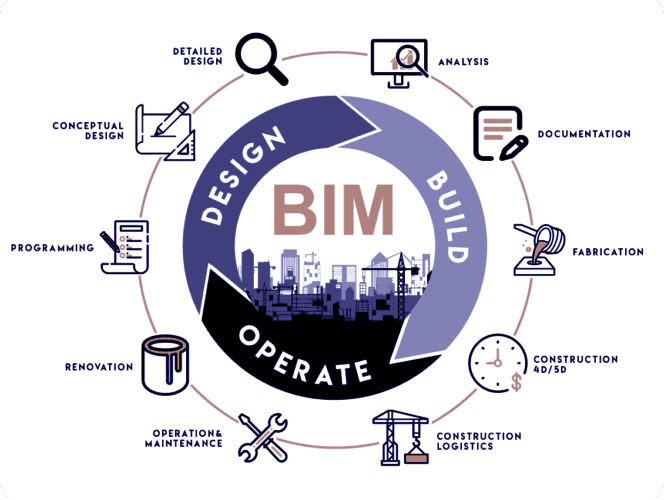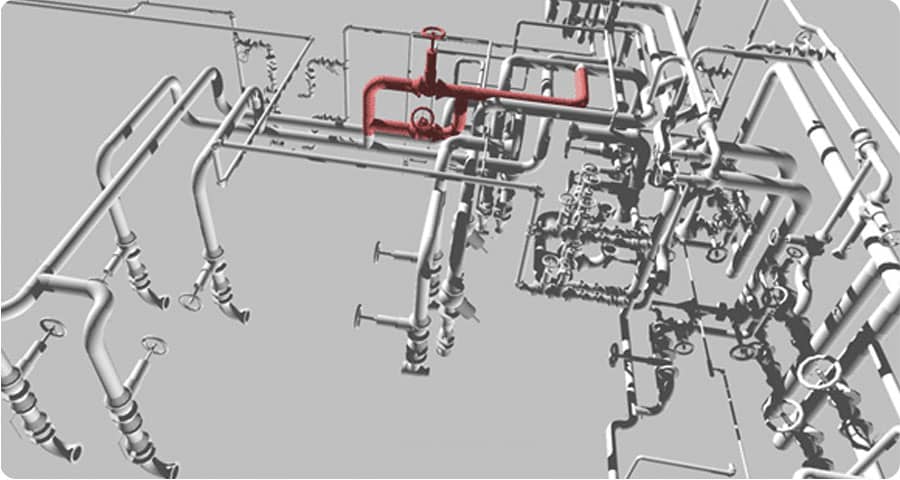
Digital Prefabrication in BIM Service
Introduction
In the fast-evolving landscape of construction and design, the amalgamation of digital technologies and traditional building methods has given rise to a revolutionary approach known as Digital Prefabrication in Building Information Modeling (BIM) service.
Understanding BIM (Building Information Modeling)
Before we dive into the realm of digital prefabrication, let's establish a foundational understanding of BIM. BIM is not merely a software tool but a comprehensive process that involves creating and managing digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of a building. It provides a collaborative platform for various stakeholders involved in a construction project.
The Evolution of Prefabrication
Prefabrication, or the assembly of building components off-site, is not a new concept. However, the integration of digital technologies has catapulted traditional prefabrication into a new era. This section will explore the historical roots of prefabrication and its evolution in the contemporary construction landscape.
Intersection of Digital Technology and Prefabrication
Digital Prefabrication is a symbiotic relationship between traditional prefabrication methods and cutting-edge digital technologies. This section will highlight how advancements in digital tools, such as 3D modeling, automation, and artificial intelligence, have transformed the way buildings are designed and constructed.
Benefits of Digital Prefabrication in BIM Service
- Enhanced Collaboration: The collaborative nature of BIM is further amplified when integrated with digital prefabrication. This subsection will elucidate how seamless communication and collaboration among stakeholders lead to more efficient project outcomes.
- Cost Efficiency: One of the compelling advantages of digital prefabrication is its impact on project costs. By streamlining processes and minimizing waste, this subsection will elaborate on how it contributes to overall cost efficiency.
- Time Savings: Time is money in the construction industry, and digital prefabrication significantly accelerates project timelines. This subsection will explore how precision in manufacturing and assembly translates to time savings on the construction site.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring the highest quality in construction projects is a priority. Digital prefabrication, through BIM integration, enhances quality assurance by minimizing errors and discrepancies. This subsection will delve into the mechanisms that contribute to superior project quality.
BIM-Integrated Prefabrication Workflows
- Virtual Design and Construction (VDC): Virtual Design and Construction is the heartbeat of BIM-integrated prefabrication. This section will elaborate on how VDC facilitates a digital representation of the entire project, allowing for in-depth planning and analysis.
- Clash Detection and Resolution: The nightmare of clashes during construction can be mitigated through BIM's clash detection capabilities. This subsection will discuss how early identification and resolution of clashes contribute to a smoother construction process.
- Quantity Takeoff and Estimation: Accurate quantity takeoffs are critical for project budgeting. Here, we'll explore how BIM's integration with digital prefabrication aids in precise quantity estimation, leading to more accurate cost projections.
- Successful Implementations: Drawing inspiration from real-world success stories, this section will showcase how various construction projects have benefited from the synergy between BIM and digital prefabrication.
Overcoming Challenges in Digital Prefabrication
- Integration Complexity: While the benefits are evident, integrating digital prefabrication into existing workflows poses challenges. This subsection will address strategies for overcoming integration complexities.
- Skill Set Requirements: Professionals need the right skills to navigate the digital prefabrication landscape. Here, we'll discuss the training and education necessary to bridge the skills gap in the industry.
- Standardization: Achieving standardization in digital prefabrication processes is crucial for widespread adoption. This subsection will explore the ongoing efforts in establishing industry standards.
Future Trends in Digital Prefabrication
- Robotics and Automation: The future of digital prefabrication holds exciting possibilities with the integration of robotics and automation. This section will delve into how these technologies are reshaping the construction industry.
- IoT (Internet of Things) Integration: The Internet of Things is increasingly becoming a game-changer in construction. Here, we'll explore how IoT integration enhances the efficiency and sustainability of digital prefabrication.
- Sustainability Practices: Sustainability is a growing concern in construction. This subsection will discuss how digital prefabrication aligns with sustainable practices, contributing to environmentally friendly building processes.
The Role of Stakeholders in Promoting Digital Prefabrication
- Architects and Designers: Architects and designers play a pivotal role in embracing and advocating for digital prefabrication. This section will highlight how their decisions influence the success of projects.
- Contractors: Contractors are on the front lines of implementing digital prefabrication. Here, we'll discuss the challenges they face and the role they play in driving adoption.
- Manufacturers: Manufacturers are key players in the prefabrication process. This subsection will explore how they can leverage digital technologies to enhance efficiency and product quality.
- Regulatory Landscape and Compliance: Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for the successful implementation of digital prefabrication. This section will shed light on existing regulations and the compliance requirements for stakeholders.
- Training and Education for Industry Professionals: To fully harness the potential of digital prefabrication, industry professionals need to stay abreast of technological advancements. This section will discuss the importance of ongoing training and education.
- ROI Analysis for Digital Prefabrication in BIM: Quantifying the return on investment is crucial for stakeholders. This section will present an analysis of the economic benefits associated with adopting digital prefabrication in BIM services.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the marriage of digital technology and prefabrication within the framework of BIM service is reshaping the construction industry. The benefits are evident, and as technology continues to evolve, so will the potential for innovation and efficiency.